Parallelising Nitro queries In single-threaded Node.js
When building Nitro9, a tool to extract BBC programme data to a relational database for offline analysis and research, it became apparent that due to Nitro’s performance, extracting just the available programmes (which does total about 85,000 including radio, podcasts and TV) would take up to twelve hours to run.
Nearly all of this time was spent waiting for network responses.
I immediately thought of parallelising the requests, something that the Open Nitro SDK currently has no support for.
My initial thoughts were to do this by pages, but this posed a few problems. Not only do you not know how many records or pages you’re going to receive until you have made the first request, even then, Nitro may simply report “more than x” records. I also hit problems where I was firing off requests far too fast, as there was now nothing to wait for, and was in danger of hitting Nitro’s rate-limiting, which is provided by the Apigee management / proxy layer.
As Node.js is single-threaded, spawning, say, four processes and letting them handle requests for a quarter of the pages each wasn’t an option. As Nitro9 was to run on Morph.io, I didn’t want to separate it into multiple processes either.
I then went back to the SDK’s API documentation to see if any of the filters could be of any use.
Here is just the relevant extract:
//...
const fProgrammesFormat = 'format';
const fProgrammesGenre = 'genre';
const fProgrammesGroup = 'group';
const fProgrammesInitialLetter = 'initial_letter';
const fProgrammesInitialLetterEnd = 'initial_letter_end';
const fProgrammesInitialLetterStart = 'initial_letter_start';
const fProgrammesInitialLetterStrict = 'initial_letter_strict';
const fProgrammesItem = 'item';
const fProgrammesMasterBrand = 'master_brand';
//...
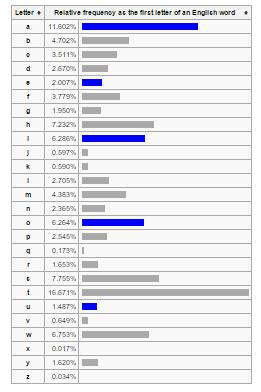 Although there were several apparently binary or multiple choice filters, none of them looked balanced enough to give a reasonable amount of
parallelisation. For example, only TV programmes can be audio-described, and most of those aren’t.
Although there were several apparently binary or multiple choice filters, none of them looked balanced enough to give a reasonable amount of
parallelisation. For example, only TV programmes can be audio-described, and most of those aren’t. fProgrammesInitialLetter however, looked
promising: filter for subset of programmes with title beginning with initial letter librarian style (ignoring leading 'The', 'An' (Welsh), etc) 0-9 a-z.
It wasn’t going to be an even distribution (see image, source
Wikipedia), but if
it was good enough for Zipf and
Yule/Simon, it was good enough for me. It seemed a workable plan and much
simpler to implement than buckets of page numbers. Simply add one filter and a for-loop, and see if sending 36 requests at once was going
to hit the rate-limiting.
// parallelize the queries by 36 times
var letters = '0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz';
for (var l in letters) {
if (letters.hasOwnProperty(l)) {
var lQuery = query.clone();
lQuery.add(api.fProgrammesInitialLetter,letters[l]);
nitro.make_request(host,path,api_key,lQuery,{Accept:'application/json'},processResponse);
}
}
My first local test looked very promising, and running it on Morph.io, completed in 42 minutes. A substantial, if not 3600% improvement.
The current version runs a little slower, as I’ve added another mixin: mProgrammesGenreGroupings but still completes in around an hour. Whether
using fProgrammesInitialLetterStrict or adding a sort would improve things further is left as an excercise for the reader.